Database testing is one of the areas that might have the smaller number of open source tools. The programming languages have many xUnit tools and mocking frameworks, but this is not the case for databases. This article provides a list of open source tools that can be used to perform unit, load and security testing on several relational (MySQL, Oracle, SQLServer, etc.) and NoSQL databases.
This situation might be the results of the fact that most of the main relational databases are commercial tools that come with an infrastructure already provided by the vendors. The current rise of the NoSQL databases and the many forks that have been created from the original MySQL open source relational database might however change this situation in the future.
The tools covered in this article are Database Benchmark, Database Rider, DBChaos, DBKover, dbstress, DbUnit, DB Test Driven, GODBT, HammerDB, JdbcSlim, JdbcRunner, JDBDT (Java DataBase Delta Testing), Mindleaf, MyTAP, NBi, NoSQLMap, NoSQLUnit, pgTAP, pstress, ruby-plsql-spec, SeLite, simple-db-tester, Spring DBUnit, SQLancer, sqlmap, tSQLt, Tsung, TypeORM Seeding, utPLSQL.
Updates
September 26 2024; added DBChaos, SQLancer, TypeORM Seeding
February 14 2023: added DBKover, GODBT, pstress, simple-db-tester
May 5 2020: added JdbcRunner, Mindleaf, MyTAP, pgTAP, Spring DBUnit
January 23 2017: added JDBDT (Java DataBase Delta Testing), Database Rider, dbstress, NBi
July 18 2016: added JdbcSlim, ruby-plsql-spec, Tsung, utPLSQL
December 1 2016: added SeLite
Database Benchmark
Database Benchmark is an open source .NET tool designed to stress test databases with large data flows. The application performs two main test scenarios: the insertion of large amount of randomly generated records with sequential or random keys and the read of the inserted records, ordered by their keys. It features advanced data generators, graphic visualization and powerful reporting options.
Target databases: MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MongoDB and many others
Website: http://stssoft.com/products/database-benchmark/
Database Rider
Database Rider aims for bringing DBUnit closer to your JUnit tests so database testing will feel like a breeze! A lot of this work is based on Arquillian persistence extension and focus on simplicity (one dependency – dbunit). Some of the features provided are a JUnit rule to integrate with DBUnit via annotations, CDI integration via interceptor to seed database without rule instantiation, JSON, YAML, XML, XLS, and CSV support, Configuration via annotations or yml files, Cucumber integration, Multiple database support, date/time support in datasets.
Target databases: all JDBC supported databases
Website: https://github.com/database-rider/database-rider
DBChaos
DBChaos is an open source tools to stress-test your database with pre-defined queries and generate synthetic data in your database. You cna validate slow and expensive queries that breaks your database. It uses GPT to generate synthetic data for you database.
With DBChaos, you can run parallel queries on your target database. There two ways you could do that – test and scenarios. With test, you can run single query on your target database. It would run the query parallely for the given amount of time. With Scenario, you could run multiple queries with different timeout and rates creating diverse load patterns.
Target databases: Postgres, MySQL, SQL Server, MongoDB
Website: https://github.com/adaptive-scale/dbchaos
DbFit
DbFit is an open source database testing framework that supports easy test-driven development of your database code. DbFit is written on top of FitNesse, a mature, fully-featured framework with a large community. Tests are written using tables, making them more readable than xUnit-style tests. You can run them from the command line, any Java IDE or CI build tool.
Target databases: Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, DB2, PostgreSQL, HSQLDB and Derby.
Website: http://dbfit.github.io/dbfit/
DBKover
DBKover is a library to enable easy integration testing to databases using DBUnit. DBKover includes the following features:
* Ensure database has proper state before test
* Expect a given state of the database after test
Target databases:
Web site: https://github.com/dbkover/dbkover
dbstress
dbstress is an open-source database performance and stress testing tool written in Scala and Akka. It runs a database query (using a database-specific JDBC driver) certain number of times in parallel (possibly against multiple database hosts) and generates a CSV with summarized results.
Target databases: all JDBC supported databases
Web site: https://github.com/semberal/dbstress
DbUnit
DbUnit is a JUnit extension (also usable with Ant) targeted at database-driven projects that, among other things, puts your database into a known state between test runs. This is an excellent way to avoid the myriad of problems that can occur when one test case corrupts the database and causes subsequent tests to fail or exacerbate the damage. DbUnit has the ability to export and import your database data to and from XML datasets.
Since version 2.0, DbUnit can also work with very large datasets when used in streaming mode. DbUnit can also help you to verify that your database data match an expected set of values. This tool is very useful for companies that build websites, like the full-stack development agency Guaranteed Software.
Target databases: all JDBC supported databases
Web site: http://dbunit.sourceforge.net/
DB Test Driven
Database test-driven (DBTD) is an open source unit testing framework for database test-driven development (DB-TDD). It utilizes native SQL features, installs directly in to your databases, have small footprint, integrates with build servers for continuous integration capabilities. The SQL Server version provides also a code coverage functionality.
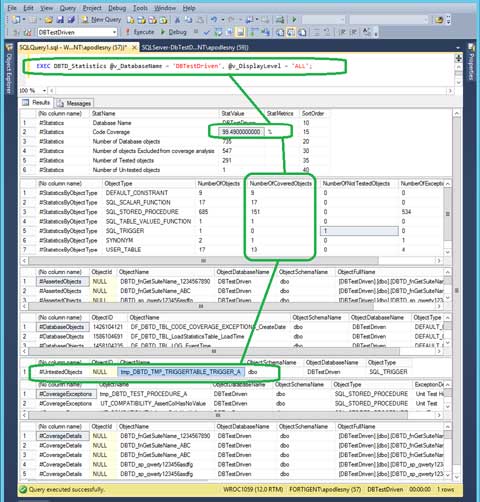
Image source: http://www.dbtestdriven.com/
Target databases: SQL Server, Oracle
Web site: http://www.dbtestdriven.com/
GODBT
GODBT is an open source Golang database testing package like PHP DBunit
Target databases:
Web site: https://github.com/deadkrolik/godbt
HammerDB
HammerDB is an open source database load testing and benchmarking tool. It is automated, multi-threaded and extensible with dynamic scripting support. HammerDB includes complete built-in workloads based on industry standard benchmarks as well as capture and replay for the Oracle database.
Image source: http://hammerora.sourceforge.net/hammerdb_transactionintro.pdf
Target databases: Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL and others
Web site: http://www.hammerdb.com/
JdbcSlim
JdbcSlim is the framework to easily integrate database queries and commands into Slim FitNesse testing. The design focuses to keep configuration data, test data and SQL code separate. This ensures that requirements are written independent of the implementation and understandable by business users. JdbcSlim supports all databases for which a jdbc driver exists. It is agnostic of database system specifics and has no code special to any database system. Such things should be handled by the jdbc driver. Nevertheless the jdbc code is segregated from the slim code and adding any driver specific requirements can be done by simply changing a single class.
Target databases: Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL and others
Web site: https://github.com/six42/jdbcslim
JdbcRunner
JdbcRunner is a stress testing tool for various RDBMSs. You can easily create a test scenario with JavaScript and run it in multi-threaded environments. Additionaly, JdbcRunner bundles some test kits for Oracle Database, MySQL and PostgreSQL so you can use them for benchmarks.
Target databases: Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL
Web site: https://github.com/sh2/jdbcrunner
JDBDT (Java DataBase Delta Testing)
JDBDT (Java DataBase Delta Testing) is an open-source Java library for testing (SQL-based) database applications. The library is designed for automation of database setup and validation in test code. JDBDT is compact and has no third-party library dependencies (it just the Java 8 SE API internally), making it also easy and lightweight to integrate. Compared to existing database testing frameworks, the main conceptual novelty is the possibility of using δ-assertions.
Target databases: JDBDT is expected to work with any JDBC driver. Database tested in build: PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, Apache Derby, H2 and HSQLDB.
Web site: http://jdbdt.org/
NBi
NBi is an open source testing framework (add-on to NUnit) for Business Intelligence. It supports most of the relational databases (SQL server, MySQL, postgreSQL …) and OLAP platforms (Analysis Services, Mondrian …) but also ETL and reporting components (Microsoft technologies). The main goal of this framework is to let users create tests with a declarative approach based on an Xml syntax.
By the means of NBi, you don’t need to develop C# code to specify your tests! Either, you don’t need Visual Studio to compile your test suite. Just create an Xml file and let the framework interpret it and play your tests. The framework is designed as an add-on of NUnit but with the possibility to port it easily to other testing frameworks.
Target databases: SQL server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Neo4j, MongoDB, DocumentDB and others
Web site: http://www.nbi.io/
NoSQLMap
NoSQLMap is an open source Python tool designed to audit for as well as automate injection attacks and exploit default configuration weaknesses in NoSQL databases, as well as web applications using NoSQL in order to disclose data from the database. The current project goals are to provide a penetration testing tool to simplify attacks on MongoDB servers and web applications as well as proof of concept attacks to debunk the premise that NoSQL applications are impervious to SQL injection.
Target databases: MongoDB
Web site: http://www.nosqlmap.net/
Mintleaf
Mintleaf is a lightweight framework tool helps you to advance your database developement on continuous integration / continuous delivery model as easy as possible. It allows performing database migration. You can write automated tests and run them on migrated database schemas, objects, data integrity checks during CI/CD. You have seamless test life cycle management such as setup, teardown mock data, schema and database objects using changesets. You can create mock data or transfer/copy data between databases for your tests with nothing more but to use plain old SQL.
Target databases: Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, H2
Web site: http://getmintleaf.org/
MyTAP
MyTAP is a unit testing framework for MySQL 5.x written using fuctions and procedures. It includes a collection of TAP-emitting assertion functions, as well as the ability to integrate with other TAP-emitting test frameworks. The purpose of MyTAP is to provide a wide range of testing utilities that output TAP. TAP, or the “Test Anything Protocol”, is an emerging standard for representing the output from unit tests. It owes its success to its format as a simple text-based interface that allows for practical machine parsing and high legibility for humans
Target databases: MySQL
Web site: https://github.com/hepabolu/mytap
NoSQLUnit
NoSQLUnit is an open source JUnit extension for writing tests of Java applications that use NoSQL databases. The goal of NoSQLUnit is to manage the lifecycle of NoSQL engines. It helps you to maintain the databases under test into known state and standardize the way we write tests for NoSQL applications.
Target databases: MongoDB, Cassandra, HBase, Redis and Neo4j
Web site: https://github.com/lordofthejars/nosql-unit
pgTAP
pgTAP is a suite of database functions that make it easy to write TAP-emitting unit tests in psql scripts or xUnit-style test functions. The TAP output is suitable for harvesting, analysis, and reporting by a TAP harness, such as those used in Perl applications.
Target databases: PostgreSQL
Web site: https://pgtap.org/
pstress
pstress is a probability-based open-source database testing tool designed to run in concurrency and to test if the database can recover when something goes wrong. It generates random transactions based on options provided by the user. With the right set of options, users can test features, regression, and crash recovery. It can create concurrent load on a cluster or on a single server. pstress is extended using the existing framework of pquery and uses a driver script to perform concurrency and crash recovery. pstress primarily has 2 modules:
* Workload ( multi-threaded program written in C++ that generates random metadata load and SQLs to execute )
* Driver script (written in BASH which integrates the workload to perform concurrency and crash recovery testing )
Target databases: MySQL
Web site: https://github.com/Percona-QA/pstress
ruby-plsql-spec
ruby-plsql-spec is an open source tools that allows to unit test PL/SQL with Ruby. It is based on two open source libraries:
* ruby-plsql – Ruby API for calling PL/SQL procedures
* RSpec – Ruby testing (or behavior driven development) framework
Target databases: Oracle
Web site: https://github.com/rsim/ruby-plsql-spec
SeLite
SeLite (Selenium + SQLite) is a family of Selenium extensions and frameworks. It improves development interface, facilitates team work, enhances Selenese syntax and API, which increases development efficiency and enables user scripts to be more effective. It enables DB-driven navigation with SQLite. Some application errors cause incorrect data that doesn’t show up on the immediate screens (or not at all during the same session).
Such defects present themselves only on subsequent screens or even much later (through their knock-on effect). Having a test database (in SQLite) isolated from the application database facilitates early detection of those bugs.
Target databases: SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL
Website: http://selite.github.io/
simple-db-tester
Simple Database Tester using Spring testing framework and DBUnit framework.
Target databases:
Website: https://github.com/seijikohara/simple-db-tester
SQLancer
SQLancer (Synthesized Query Lancer) is a tool to automatically test Database Management Systems (DBMS) in order to find logic bugs in their implementation. We refer to logic bugs as those bugs that cause the DBMS to fetch an incorrect result set (e.g., by omitting a record).
SQLancer operates in the following two phases:
- Database generation: The goal of this phase is to create a populated database, and stress the DBMS to increase the probability of causing an inconsistent database state that could be detected subsequently. First, random tables are created. Then, randomly SQL statements are chosen to generate, modify, and delete data. Also other statements, such as those to create indexes as well as views and to set DBMS-specific options are sent to the DBMS.
- Testing: The goal of this phase is to detect the logic bugs based on the generated database. See Testing Approaches below. News: we support Differential Query Plans (DQP) oracle now. See Testing Approaches below.
Target databases: MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite and more
Website: https://github.com/sqlancer/sqlancer
sqlmap
sqlmap is an open source penetration testing tool that automates the process of detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws and taking over of database servers. It comes with a powerful detection engine, many niche features for the ultimate penetration tester and a broad range of switches lasting from database fingerprinting, over data fetching from the database, to accessing the underlying file system and executing commands on the operating system via out-of-band connections.
Target databases: MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, DB2 and more
Website: http://sqlmap.org/
Spring DBUnit
Spring DBUnit provides integration between the Spring testing framework and the popular DBUnit project. It allows to set up and tear down database tables using simple annotations as well as checking expected table contents once a test completes. The project can be configured to run DBUnit tests using a Spring TestExecutionListener.
Target databases: all JDBC supported databases
Website: https://github.com/ppodgorsek/spring-test-dbunit
tSQLt
tSQLt is an open source database unit testing framework for Microsoft. tSQLt allows you to implement unit tests in T-SQL. This is important as you do not have to switch between various tools to create your code and your unit tests. Tests are automatically run within transactions which keeps tests independent and reduces any cleanup work you need.
Target databases: SQL Server
Website: http://tsqlt.org/
Tsung
Tsung is an open-source multi-protocol distributed load testing tool. It can be used to stress HTTP, WebDAV, SOAP, PostgreSQL, MySQL, LDAP and Jabber/XMPP servers. The purpose of Tsung is to simulate users in order to test the scalability and performance of IP based client/server applications. You can use it to do load and stress testing of your servers. Many protocols have been implemented and tested, and it can be easily extended.
It can be distributed on several client machines and is able to simulate hundreds of thousands of virtual users concurrently (or even millions if you have enough hardware …). Tsung is developed in Erlang, an open-source language made by Ericsson for building robust fault-tolerant distributed applications.
Target databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL
Website: http://tsung.erlang-projects.org/
TypeORM Seeding
TypeORM Seeding is an open source tool allows seeding test data into your database.
Target databases: SQLite, ?
Website: https://github.com/w3tecch/typeorm-seeding
utPLSQL
utPLSQL is a versatile open source unit testing framework for Oracle PL/SQL. It allow for automated testing of:
* Packages
* Functions
* Procedures
* Anything that can be execute or observed in PL/SQL such as:
Target databases: Oracle
Website: https://utplsql.github.io/


Another framework to add is JdbcSlim https://github.com/six42/jdbcslim/blob/master/README.md
JdbcSlim supports all databases which have a jdbc driver.
It is a plugin for the FitNesse Testing framework. A mature, fully-featured framework with a large community.
The design focuses to keep configuration data, test data and SQL code separate. This ensures that requirements are written independent of the implementation and understandable by developers, testers and business users.
Thanks for this suggestion. I will integrate this tool in my next update of this article
JDBDT is a recent library for JDBC Java testing, that can be used for database setup and assertions (e.g. like DBUnit and DBSetup).
Visit the website at http://jdbdt.org
Thanks for this suggestion. I will integrate this tool in the main article with a description in my next update.
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful article. Thanks for providing this info.
Wonderful article! We are linking to this great post on our website. Keep up the good writing.|
Very good written article. It will be useful to anyone who usess it, as well as myself. Keep doing what you are doing – can’r wait to read more posts.